# Evidence sections: Evaluate annotation and studies
In FULL (default) mode, the main view of the CLASSIFICATION page contains a number of different sections (shown here as collapsed):
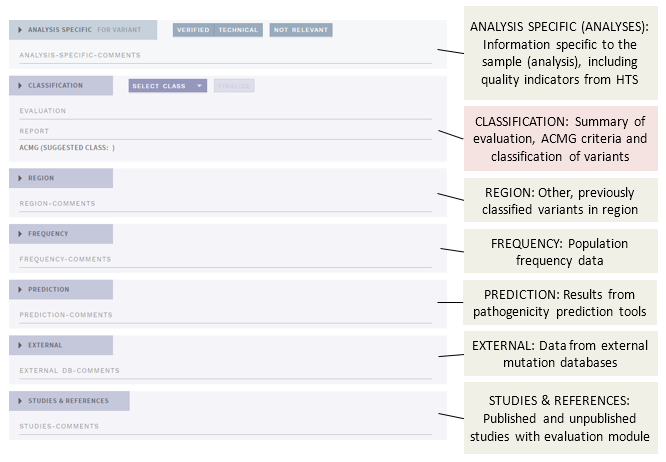
The different sections presenting annotation evidence are described below, see the separate page for the Classification section.
# Analysis specific (ANALYSES only)
This section is for information and actions specific to the variant as observed in the current sample (analysis), and displays indicators of the quality of the variant calling (HTS data, ANALYSES mode only).
NOTE
This is the only section on this page that is specific to the sample (analysis), all other sections are tied to the variant interpretation, which is independent of samples. This also means that any comments you add here will be visible in this analysis only.
# Quality information
Quality information is tied to a particular sample, and is therefore only available in ANALYSES mode. In addition, only information from HTS data is provided. The following quality parameters from the VCF file (opens new window) are shown :
Filter:
PASSif all filters have passed, otherwise list filters that failedQuality: Variant calling quality
- Phred-scaled probability that a REF/ALT polymorphism exists at this site given sequencing data
- 10 = 1 in 10 chance of error, 100 = 1 in 10^10 chance of error
GQ: Genotype quality
- Derived from PL (see below), comparing the difference between the second lowest PL to the lowest PL (0)
- Value is capped at 99
PL: Phred-scaled genotype likelihood (opens new window)
- Values are given for genotypes [REF/REF, REF/ALT, ALT/ALT]
- Most likely genotype is 0; the higher the other values, the less likely they are true
Depth: Number of reads covering the site
Ratio: Number of reads covering each allele, with ratio for variant allele/total
# De novo variants
In addition to the above, for de novo variants (marked with a D tag in the sidebar), a P(de novo) value (0-1) is shown for the proband, indicating the posterior probability that the de novo call is true. For details, see Vigeland et al. 2016 (opens new window).
# Warning: Needs verification
HTS variants with quality issues are marked with NEEDS VERIFICATION in red in the QUALITY card. This is shown if any of the following conditions are true:
- Not an SNP (e.g. insertion/deletion).
- Filter not
PASS - Depth <20
- Allele ratio ≤0.9 if homozygous, ≤0.3 or ≥0.7 if heterozygous
# Mark as verified/technical/not relevant
In the header of the ANALYSIS SPECIFIC section, you can mark variants as VERIFIED, TECHNICAL or NOT RELEVANT:
VERIFIEDmeans the variant has been verified by an independent method (e.g. Sanger) in this sample. This adds a greenVtag in the "Q" column of the side bar.TECHNICALmeans the variant is a false variant call in this sample (analysis). This adds a redTtag in the "Q" column of the side bar and moves the variant to the TECHNICAL VARIANTS side bar section.NOT RELEVANTmeans the variant should be disregarded in this analysis, e.g. due to a mismatch with the phenotype. This moves the variant to the NOT RELEVANT VARIANTS side bar section.
TIP
Variants marked as TECHNICAL or NOT RELEVANT can, depending on the your configuration, be left without a selected class upon finalization of the analysis.
# Region
This section displays other, previously classified variants within a predefined, genomic distance from the selected variant. Click on the link to open the other variant evaluation in a new tab.
If there are more than a preset max number of variants (e.g., 10), only the closest variants are shown.
# Frequency
This section displays population frequencies reported in external or internal datasets (if any). Note that variants with a population frequency exceeding the threshold for ACMG criterion BA1 have already been filtered out.
# Included datasets
- GnomAD exomes and genomes (opens new window)
- ExAC (opens new window) (NB: partly deprecated, most samples are included in gnomAD)
- InDB: In-house frequency database.
- dbSNP (opens new window)
NOTE
Any dbSNP entry that has positional overlap with the current variant is reported, and therefore may not contain the exact same variant/allele. If you use this data, you should check the dbSNP entry to verify that it has the same variant as in your sample.
Variants with quality issues reported in gnomAD display a warning in the gnomAD cards.
# Prediction
This section displays various predicted effects of the variant.
# Included predictions
# VEP consequence
Variant Effect Predictor (VEP) (opens new window) provides basic information about the location and expected effect of a variant within a transcript and protein. VEP uses Sequence Ontology terms (opens new window).
By default, only effects in the default transcript(s) specified in the gene panel are shown. However, if there are worse consequences in other, alternative RefSeq (NM_) transcripts, this will also be displayed together with a warning. To view consequences in all alternative RefSeq transcripts, click the given consequence(s).
# Add predictions
Add other types of predictions by clicking the ADD PREDICTION button:
The choices you make here are meant as “keywords”, and any details important for evaluating the choices made should always be added to the PREDICTION-COMMENTS field. Choices made here result in suggestions for relevant ACMG codes in the CLASSIFICATION section, but you still need to approve/add individual codes before final classification.
NOTE
The DOMAIN and REPEAT options are also available in the reference evaluation module (see below), and should be added there if you have a specific reference to attach this information to.
The manual options are:
ORTHOLOG CONSERVATION
CONSERVED: the amino acid is highly conserved in orthologsNON-CONSERVED: the amino acid is not conserved in orthologs
PARALOG CONSERVATION
CONSERVED: the amino acid is highly conserved in paralogsNON-CONSERVED: the amino acid is not conserved in paralogs
DNA CONSERVATION
CONSERVED: the DNA nucleotide is highly conservedNON-CONSERVED: the DNA nucleotide is not conserved
DOMAIN
CRITICAL FUNCTIONAL DOMAIN: the variant is located in a critical functional domainCRITICAL FUNCTIONAL AMINO ACID: the function of the reference amino acid is known to be critical
REPEAT
REPEAT REGION: the variant is located in a repeat region.NON-REPEAT REGION: the variant is located in a non-repeat region
SPLICE SITE EFFECT
SPLICE SITE LOST: the variant is predicted to cause the loss of an authentic splice siteDE NOVO SPLICE SITE: the variant is predicted to cause the creation of a novel splice siteNO SPLICE SITE EFFECT: the variant is predicted to have no effect on splicing
Remember to SAVE (top right) once you are done.
# External
This section shows annotation from external databases, currently including HGMD Pro and ClinVar.
# Included databases
# Add data from other external databases
If you want to add results from other databases (various LSDBs, depending on the gene), press the ADD EXTERNAL DB button:
In the pop-up, select from the dropdown for each database you want to add from. For pre-specified databases, there will be a Visit database link to the right, which will take you to the corresponding database and gene. Choices for all databases except OTHER (which is free text) are:
Unambiguous classification:
- Pathogenic: Class 5 or similar
- Likely pathogenic: Class 4 or similar
- Uncertain significance: Class 3 or similar
- Likely benign: Class 2 or similar
- Benign: Class 1 or similar
Other:
- Conflicting: Conflicting classes reported
- Indirectly relevant: Variant is not the same, but has indirect relevance
- Nothing found: No entries found in database
- Other: None of the choices above are applicable
Remember to SAVE (top right) once you are done.
# Studies & references
This section contains literature references describing the selected variant. The references have been automatically retrieved from the annotation, but you can also add studies yourself.
# Reference evaluation
Evaluate or ignore a reference by pressing one of the corresponding buttons:
TIP
Recurring, generic or otherwise irrelevant references from the annotation can automatically be ignored by changing the configuration by a system administrator.
When a choice/evaluation already has been made, the EVALUATE button changes to RE-EVALUATE.
The STUDIES-COMMENTS field at the top should be used for summarizing findings and comments from the individual reference evaluation forms:
# Reference evaluation form
The EVALUATE button will bring up the reference evaluation form. Help text for the different options provided here is available by holding the mouse cursor over the header/question.
The options in the form are meant as a guide, and you should always make a comment (at the bottom of the form) summarizing any points from the reference that will be important for the classification of the variant. This comment is also visible in the reference list and can be directly edited here once an evaluation has been performed.
# Section cards
Evaluated/new references are placed in separate cards (only non-empty cards are shown):
EVALUATED: References marked with RELEVANCE:
YESorINDIRECTLYin the evaluation form.PENDING: New references (no evaluation has been performed).
NOT RELEVANT: References marked with RELEVANCE:
NOin the evaluation form. Note that this should only be used when the reference has actually been reviewed, but found not to contain relevant evidence.IGNORED: References marked with either the
IGNOREbutton or RELEVANCE:IGNOREin the evaluation form. This card is hidden by default; To review, press theSHOW IGNOREDbutton:These references may be added back by clicking the `RE-EVALUATE` button and changing to RELEVANCE: `YES` or `INDIRECTLY`.
# Add studies
If you have found other studies/references that aren’t already in the list, you can add them by clicking the ADD STUDIES button:
The resulting dialogue lets you add studies in one of three ways:
SEARCH: Search the internal database for studies that have already been added but not connected to the current variant, then click ADD next to a positive search result.
PUBMED: Add reference data from PubMed. To add a reference:
On the PubMed page for that reference, download the details with
Save- "Format: PubMed" andCreate file: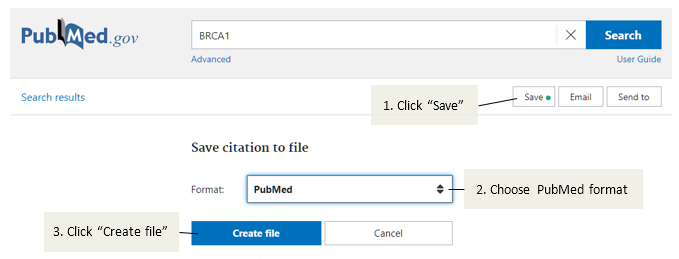
Open the file that is downloaded, copy the entire contents and paste it into the
RAW PUBMED DATAfield in ELLA.
MANUAL: Add studies manually, either PUBLISHED or UNPUBLISHED (e.g., in-house) studies. Fields marked with a * are mandatory.